This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 1g | $280 | Check With Us |
| 2g | $450 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $750 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3561 CAS #: 8025-81-8 Purity ≥ 98%
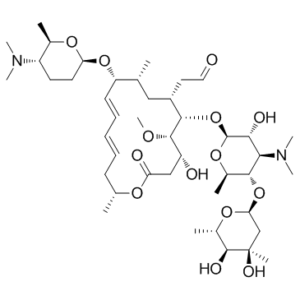
Description: Spiramycin (HSDB7027; HSDB-7027; Rovamycin) is naturally occurring and clinically important 16-member macrolide antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces ambofaciens. It has activity against bacteria and Toxoplasma gondii, and also has antiparasitic effect. Spiramycin is composed of a 16-member lactone ring, on which three sugars (mycaminose, forosamine, and mycarose) are attached. Biosynthetic studies have established that the earliest lactonic intermediate in spiramycin biosynthesis, the macrolactone platenolide I, is synthesized by a type I modular polyketide synthase (PKS). Platenolide I then undergoes a series of post-PKS tailoring reactions yielding the final products, spiramycins I, II, and III.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 843.05 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₄₃H₇₄N₂O₁₄ |
| CAS No. | 8025-81-8 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| SMILES Code | O=CC[C@@H]1[C@H](O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C)[C@@H](O[C@@H]3O[C@@H](C)[C@H](O)C(C)(O)C3)[C@H](N(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](OC)[C@H](O)CC(O[C@H](C)C/C=C/C=C/[C@H](O[C@@H]4O[C@H](C)[C@@H](N(C)C)CC4)[C@H](C)C1)=O |
| Synonyms | HSDB-7027; Rovamycin; HSDB7027; HSDB 7027 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Spiramycin (24 hours; 1-1000 μM; T. gondii infected HeLa cells and HeLa cells) treatment reduces the cytotoxicity, and shows anti-Toxoplasma gondii activity, with IC50 values of 189 μM for HeLa cells; and 262 μM for T. gondii-infected HeLa cells. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Spiramycin (100 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; every day; for 4 days; female KM mice) treatment reduces the number of tachyzoites, and reduces hepatotoxicity and significantly enhances antioxidative effects. Spiramycin treatment also decreases in the degree of granulomatous inflammation in the liver. | |
| Animal model | 36 female KM mice with T.gondii | |
| Dosages | 100 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Intraperitoneal injection; every day; for 4 days |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.1862 mL | 5.9308 mL | 11.8617 mL | 23.7234 mL |
| 5mM | 0.2372 mL | 1.1862 mL | 2.3723 mL | 4.7447 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1186 mL | 0.5931 mL | 1.1862 mL | 2.3723 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0593 mL | 0.2965 mL | 0.5931 mL | 1.1862 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































