This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $980 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1650 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $2475 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V3217 CAS #: 952849-76-2 Purity ≥ 98%
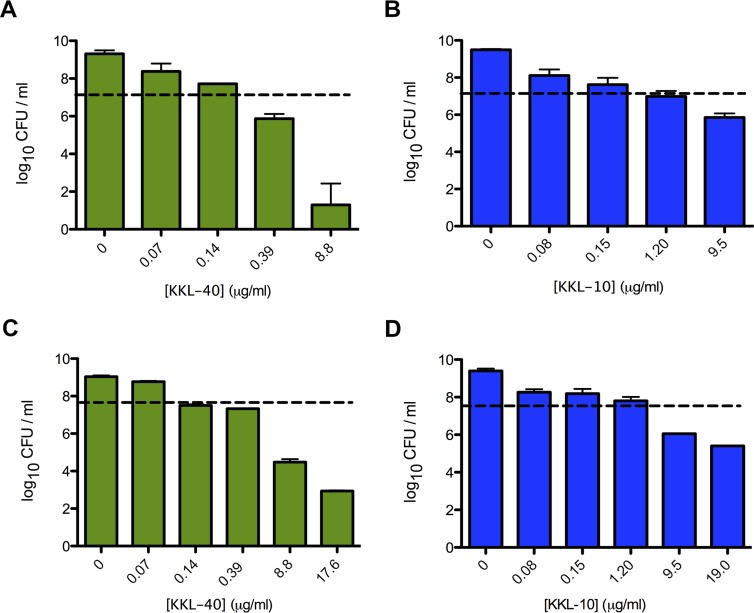
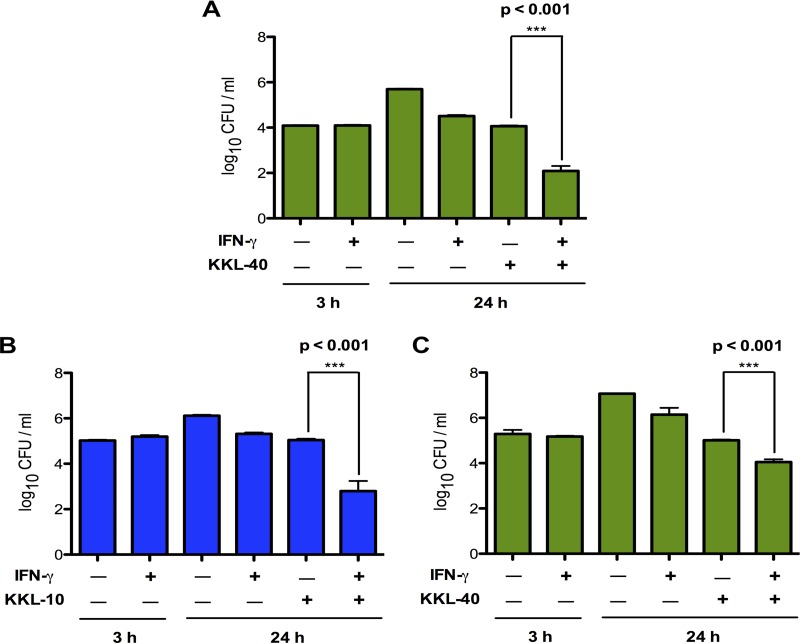
Description: KL-10 is a small-molecule ribosome rescue inhibitor that possesses a broad-spectrum of antimicrobial activity against bacteria. KKL-10 exhibited exceptional antimicrobial activity against both attenuated and fully virulent strains of F. tularensis in vitro and during ex vivo infection. Addition of KKL-10 to macrophages or liver cells at any time after infection by F. tularensis prevented further bacterial proliferation. When macrophages were stimulated with the proinflammatory cytokine gamma interferon before being infected by F. tularensis, addition of KKL-10 reduced intracellular bacteria by >99%, indicating that the combination of cytokine-induced stress and a nonfunctional ribosome rescue pathway is fatal to F. tularensis. KKL-10 was not cytotoxic to eukaryotic cells in culture. Therefore, KKL-10 is a good lead compound for antibiotic development.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 364.22 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H10BrN3O2S |
| CAS No. | 952849-76-2 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: > 10mMr |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
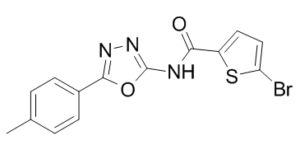
| SMILES Code | O=C(C1=CC=C(Br)S1)NC2=NN=C(C3=CC=C(C)C=C3)O2 |
| Synonyms | KKL10; KKL 10; KKL-10 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: KL-10 is a small-molecule ribosome rescue inhibitor that possesses a broad-spectrum of antimicrobial activity against bacteria. KKL-10 exhibited exceptional antimicrobial activity against both attenuated and fully virulent strains of F. tularensis in vitro and during ex vivo infection. Addition of KKL-10 to macrophages or liver cells at any time after infection by F. tularensis prevented further bacterial proliferation. When macrophages were stimulated with the proinflammatory cytokine gamma interferon before being infected by F. tularensis, addition of KKL-10 reduced intracellular bacteria by >99%, indicating that the combination of cytokine-induced stress and a nonfunctional ribosome rescue pathway is fatal to F. tularensis. KKL-10 was not cytotoxic to eukaryotic cells in culture. Therefore, KKL-10 is a good lead compound for antibiotic development. Kinase Assay: For MIC assays, triplicate 2-fold serial dilutions of each compound were made in cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth (CAMHB) and added to a 96-well microtiter plate. Stocks of each compound were prepared in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Overnight cultures of LVS or Schu S4 were diluted to an OD600 of 0.05 in CAMHB to a final volume of 0.1 ml and added directly to the diluted compounds. The microtiter plates were incubated overnight (∼18 h) at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. Bacterial growth was monitored by measuring the optical density at 600 nm. The MIC was determined by observing the lowest concentration at which the compound prevented a significant increase in the optical density. To enumerate F. tularensis after exposure to various concentrations of KKL-10 or KKL-40, the contents of the MIC assay microtiter plate were removed and plated on chocolate agar at appropriate dilutions. After incubation for 48 h at 37°C and 5% CO2, colonies were counted to calculate CFU per milliliter. Cell Assay: Cytotoxicity assays were performed using RAW 264.7 cells and a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay kit (Pierce Biochemicals, USA) following the manufacturer's instructions. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | The hind legs of euthanized C57 mice were skinned and removed at the hip joint, and feet and excess muscle tissue were removed. Marrow was liberated by removing the femurs proximal to each joint and crushing them in a 70-μm nylon mesh filter in 5 ml phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) using a sterile pestle. The marrow was added to conical tubes and centrifuged at 400 × g for 10 min at room temperature. The supernatant was discarded, and the pellet was resuspended in Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM) (ThermoFisher, USA). The cells were plated in 100-mm petri dishes at a density of 4 × 105 cells/ml in 10 ml complete macrophage differentiation medium (DMEM plus 20% L929 cell supernatant containing macrophage colony-stimulating factor [M-CSF]). The cells were supplemented with an additional 5 ml of medium on days 1 and 3, and bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were harvested on day 7. | |
| Animal model | C57 mice |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.7456 mL | 13.7280 mL | 27.4559 mL | 54.9119 mL |
| 5mM | 0.5491 mL | 2.7456 mL | 5.4912 mL | 10.9824 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2746 mL | 1.3728 mL | 2.7456 mL | 5.4912 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1373 mL | 0.6864 mL | 1.3728 mL | 2.7456 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.