This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | $850 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $1400 | Check With Us |
| 5g | $3525 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V1926 CAS #: 58-58-2 Purity ≥ 98%
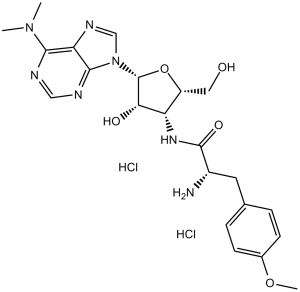
Description: Puromycin 2HCl (CL13900), an analog of aminoacyl-tRNA (anaminonucleoside), is a potent antibiotic which acts as a protein synthesis inhibitor. It inhibits the incorporation of aminoacyl-tRNA into the C-terminal on a synthesizing polypeptide, resulting in the premature termination of the polypeptide chain. Puromycin is toxic to the growth of various eukaryote cells including mammalian cells. Concentrations of puromycin sufficient to inhibit the cell growth of mammalian cells range from 0.5-10 μg/ml. IC90s for puromycin to inhibit the growth of Plasmodium falciparum and Giardia lamblia are 60 ng/ml and 54 μg/ml, respectively.
References: [1]. Nathans D, et al. Puromycin inhibition of protein synthesis: incorporation of puromycin intopeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:585-92.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 544.43 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H29N7O5.2HCl |
| CAS No. | 58-58-2 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (183.7 mM)r |
| Water: 100 mg/mL (183.7 mM)r | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
| SMILES Code | O=C(N[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N(C)C)N=CN=C23)[C@@H]1O)[C@@H](N)CC4=CC=C(OC)C=C4.[H]Cl.[H]Cl |
| Synonyms | Puromycin Dihydrochloride; Puromycin 2HCl; CL13900 2HCl; CL-13900 dihydrochloride; CL 13900 dihydrochloride; Puromycine; NSC-3055; NSC3055; NSC 3055 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: The antibiotic puromycin is produced by the actinoniycete, Streptornyces alboniger, and has been used as a tool for studying protein synthesis in a number of systems. Puromycin can be used for the selection of recombinant cells from noncultured cells. Cell Assay: When treated with puromycin dihydrochloride at different concentrations, the growth rates of T. thermophila changed. In the first 24 h, puromycin dihydrochloride at a concentration of 50 µg/ml reduced the growth rate by 80%, but did not completely block the cell growth; until 72 h, there was a gradual cell number increase. At 100 μg/ml, puromycin dihydrochloride completely blocked the cell growth; in the first 48 h under this condition, almost all of the cells died, surviving cells grew rapidly after 48 h. Puromycin dihydrochloride at 150 μg/ml completely inhibited the cell growth for 72 h. By 72 h, the majority of cells died, and then surviving cells grew. Puromycin dihydrochloride at 200 μg/ml made almost all the cells die by 48 h, and hence no survivors appeared. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In animals of 25 days old, 180 or 120 min of previous exposure to puromycin dihydrochloride inhibited subsequent amino acid transport. In animals of 50 days old, however, puromycin dihydrochloride failed to inhibit α-aminoisobutyric acid uptake. |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.8368 mL | 9.1839 mL | 18.3678 mL | 36.7357 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3674 mL | 1.8368 mL | 3.6736 mL | 7.3471 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1837 mL | 0.9184 mL | 1.8368 mL | 3.6736 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0918 mL | 0.4592 mL | 0.9184 mL | 1.8368 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































