This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 25g | $350 | Check With Us |
| 50g | $600 | Check With Us |
| 100g | $900 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V0697 CAS #: 24169-02-6 Purity ≥ 98%
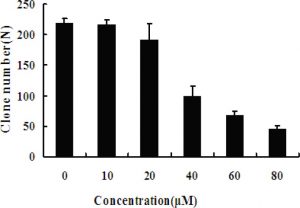
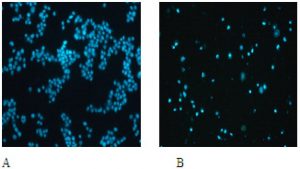
Description: Econazole Nitrate (formerly also known as NSC-243115; SQ-13050; Spectazole) is a potent calcium channel blocker/CCB used as an imidazole-based antifungal medicine against infections caused by fungus. It was approved in 1974 for treating a variety of fungal skin infections such as athlete's foot, jock itch, and ringworm. Econazole nitrate is an effective inducer of micronuclei over a narrow dose range in cell lines V79, XEM2 and XEMd-MZ (expresses CYP1A2). Econazole nitrate inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner by MTT method and colony forming assay. Econazole nitrate results in typical characteristics of apoptosis including the morphological changes and DNA fragmentation in MCF-7 cells.
References: [1]. Thienpont, D., et al., Bilogical and toxicological properties of econazole, a broad-spectrum antimycotic. Arzneimittelforschung, 1975. 25(2): p. 224-30.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 444.7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H15Cl3N2O.HNO3 |
| CAS No. | 24169-02-6 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 89 mg/mL (200.1 mM)r |
| Water: <1 mg/mLr | |
| Ethanol: 5 mg/mL (11.2 mM) | |
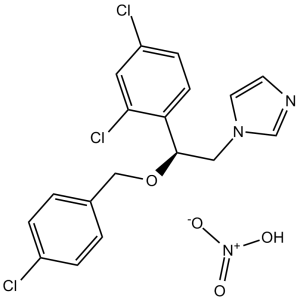
| SMILES Code | C1=CC(=CC=C1COC(CN2C=CN=C2)C3=C(C=C(C=C3)Cl)Cl)Cl.[N+](=O)(O)[O-] |
| Synonyms | NSC 243115; NSC-243115; NSC243115; Econazole Nitrate; R 14,827; R 14827; Spectazole; SQ 13050; SQ13050; SQ-13050; Ecoza; epi-Pevaryl; Gyno-pevaryl; Ifenec. |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Econazole nitrate is an effective inducer of micronuclei over a narrow dose range in cell lines V79, XEM2 and XEMd-MZ (expresses CYP1A2). Econazole nitrate inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner by MTT method and colony forming assay. Econazole nitrate results in typical characteristics of apoptosis including the morphological changes and DNA fragmentation in MCF-7 cells. Econazole nitrate results in the decrease expression of procaspase-3, procaspase-9 and bcl-2. Econazole inhibits ADP-ribose-activated currents in HEK-293 cells expressing recombinant human TRPM2 (hTRPM2). Econazole produces an essentially complete inhibition of the TRPM2-mediated current. Econazole (25-50 mM) partially inhibits capacitative Ca2+ entry induced by cyclopiazonic acid, another endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump inhibitor. Econazole induces Ca2+ influx via two separate pathways: one is sensitive to La3+, the other is not. Econazole reversibly inhibits (Bu)(2)cAMP-stimulated progesterone production in a dose- and time-dependent manner in MA-10 cells without affecting total protein synthesis or P450(scc) and 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3beta-HSD) enzyme expression or activity. Econazole is a store-operated Ca2+ channel antagonist which induces cytotoxic cell death of leukemia. Econazole (5-20 mM) arrests human colon cancer cells at the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. Econazole induces COLO 205 cells apoptosis evidenced by ladder formation in DNA fragmentation assay and sub-G1 peak. |
|---|
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.2487 mL | 11.2435 mL | 22.4871 mL | 44.9741 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4497 mL | 2.2487 mL | 4.4974 mL | 8.9948 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2249 mL | 1.1244 mL | 2.2487 mL | 4.4974 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1124 mL | 0.5622 mL | 1.1244 mL | 2.2487 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.