This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $600 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $800 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $1200 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V2511 CAS #: 179463-17-3 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Caspofungin acetate (formerly known as MK-0991; trade name: Cancidas), a cyclic lipopeptide, is a new class of antifungal drug. It is a semi-synthetic analogue of pneumocandin B0 with improved water solubility, a significant limitation in the development of the echinocandin class as pharmaceuticals. Caspofungin acts by inhibiting the synthesis of β (1,3)-D-glucan, an essential component of the cell wall of susceptible fungi. Incubation ofA. fumigatuwith a single dose of caspofungin affected the same proportion of apical and subapical branching cells for up to 72 h.The cells at the active centers for new cell wall synthesis withinA. fumigateshyphae are killed when they are exposed to caspofungin.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 1213.42 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C56H96N10O19 |
| CAS No. | 179463-17-3 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (82.4 mM)r |
| Water: N/Ar | |
| Ethanol: 100 mg/mL (82.4 mM) | |
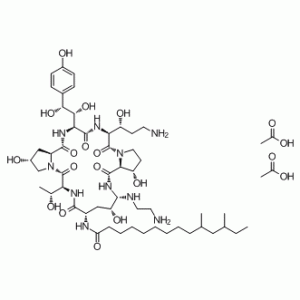
| SMILES Code | CC[C@@H](C)C[C@@H](C)CCCCCCCCC(N[C@@H]1C(N[C@@H]([C@H](O)C)C(N2[C@](C[C@@H](O)C2)([H])C(N[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C3=CC=C(O)C=C3)C(N[C@H]([C@H](O)CCN)C(N4[C@]([C@@H](O)CC4)([H])C(N[C@H](NCCN)[C@@H](O)C1)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O.CC(O)=O.CC(O)=O |
| Synonyms | MK-0991; L-743872; MK 0991; L743872; MK0991; L 743872; trade name: Cancidas. |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: Incubation ofA. fumigatuwith a single dose of caspofungin affected the same proportion of apical and subapical branching cells for up to 72 h.The cells at the active centers for new cell wall synthesis withinA. fumigateshyphae are killed when they are exposed to caspofungin. Caspofungin acetate irreversibly inhibited the enzyme 1,3-β-D-glucan synthase, preventing the formation of glucan polymers and disrupting the integrity of the fungal cell wall. The elimination half-life of caspofungin acetate was 9-10 hours. Caspofungin showed activity againstAspergillusspp. as well as a variety ofCandidaspp. Growth kinetic studies of caspofungin acetate against Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis isolates showed that caspofungin acetate exhibited fungicidal activity (i.e., a 99% reduction in viability) within 3 to 7 h at concentrations ranging from 0.06 to 1 μg/ml (0.25 to 4 times the MIC)[4].The minimal inhibitory concentration for 90% inhibition of Candida species by caspofungin acetate were as follows:C. albicans 0.5 μg/mL (range, 0.25-0.5), C. glabrata 1.0 μg/mL (range, 0.25-2.0), C. tropicalis 1.0 μg/mL (range, 0.25-1.0), C. parapsilosis 0.5 μg/mL (range, 0.25-1.0), and C. krusei 2.0 μg/mL (range, 0.5-2.0). Kinase Assay: caspofungin Acetate is an antifungal drug that noncompetitively inhibits 1,3-β-d glucan synthase activity. Cell Assay: Caspofungin suppressed the synthesis of cell wall β-1,3-glucan, which triggered a compensatory stimulation of chitin synthesis. Caspofungin induced morphological changes in Aspergillus fumigates. Moreover, Treatment with caspofungin induced ChsG-dependent upregulation of chitin synthesis and the formation of chitin-rich microcolonies in Aspergillus fumigates. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Mice injected with caspofungin at vitreal concentrations from 0.41 to 4.1 μM do not have significant alterations in their ERG waveforms, and their retinas have no detectable morphologic changes or loss of cells. At the vitreal concentration of 41 μM, caspofungin reduces the amplitudes of the a-waves, b-waves, and scotopic threshold responses of the ERG and also produces a decrease in the number of cells in the ganglion cell layer. Caspofungin (8 mg/kg) or amphotericin B at 1 mg/kg given i.p. once daily for 7 days beginning at 30 h after infection resulted in 100% survival through day 28 relative to vehicle control treatment, which results in 100% mortality by day 11 after infectious challenge. Caspofungin reduces recovery of viable Candida from kidney and brain tissues compared to vehicle control treatment on day 5, when control burden peaked. Caspofungin-treated mice dosed with 2 mg/kg or greater have significantly lower brain burden than amphotericin-B-treated mice at day 5. Amphotericin B and caspofungin treatment reduce kidney fungal burden by 1.7 log CFU/g and 2.46 to 3.64 log CFU/g, respectively. | |
| Animal model | Mice | |
| Formulation | Complement component 5-deficient DBA/2N mice | |
| Dosages | 1, 2, 4 and 8 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Intraperitoneal injection; daily, for 7 days |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 0.8241 mL | 4.1206 mL | 8.2412 mL | 16.4823 mL |
| 5mM | 0.1648 mL | 0.8241 mL | 1.6482 mL | 3.2965 mL |
| 10mM | 0.0824 mL | 0.4121 mL | 0.8241 mL | 1.6482 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0412 mL | 0.2060 mL | 0.4121 mL | 0.8241 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































