This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 5g | $450 | Check With Us |
| 10g | $650 | Check With Us |
| 20g | $975 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V28840 CAS #: 9041-08-1 Purity ≥ 99%
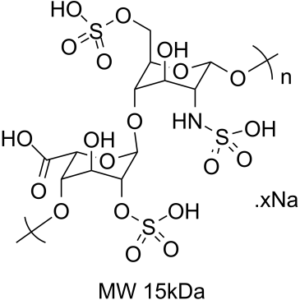
Description: Heparin sodium salt (MW 15kDa), a polymerized Heparin with a molecular weight of 15kDa, is an anticoagulant which binds reversibly to antithrombin III (ATIII) and greatly accelerates the rate at which ATIII inactivates coagulation enzymes thrombin factor IIa and factor Xa.
References: Capila I, et al. Heparin-protein interactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2002 Feb 1;41(3):391-412.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 6117(Average) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | (C14H25NO20S3)n.xNa |
| CAS No. | 9041-08-1 |
| Synonyms | Heparin sodium salt; Sodium heparin; Sodium heparinate |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Heparin is a potent anticoagulant drug based on its ability to accelerate the rate at which antithrombin inhibits serine proteases in the blood coagulation cascade. Heparin and the structurally related heparan sulfate are complex linear polymers comprised of a mixture of chains of different length, having variable sequences. Heparin interactes most tightly with peptides containing a complementary binding site of high positive charge density. Heparin and heparan sulfate predominantly exhibit linear helical secondary structures with sulfo and carboxyl groups displayed at defined intervals and in defined orientations along the polysaccharide backbone. Heparin resembles DNA as both are highly charged linear polymers that behave as polyelectrolytes. Heparin is believed to function as an anticoagulant primarily through its interaction with AT III by enhancing AT-III-mediated inhibition of blood coagulation factors, including thrombin and factor Xa. Heparin binds to AT III and thrombin in a ternary complex, increasing the bimolecular rate constant for the inhibition of thrombin by a factor of 2000. Heparin is principally located in the granules of tissue mast cells that are closely associated with the immune response. Heparin makes numerous contacts with both FGF-2 and FGFR-1 stabilizing FGF–FGFR binding. Heparin also makes contacts with the FGFR-1 of the adjacent FGF–FGFR complex, thus seeming to promote FGFR dimerization. |
|---|
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































