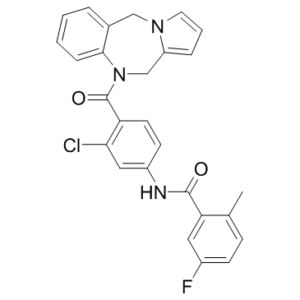
Lixivaptan
This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
For small sizes, please check our retail website as below: www.invivochem.com
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 250mg | $1160 | Check With Us |
| 500mg | $1650 | Check With Us |
| 1g | $2475 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V4748 CAS #: 168079-32-1 Purity ≥ 98%
Description: Lixivaptan (formerly known as VPA-985, WAY-VPA 985) is a novel, potent, selective and orally bioactive non-peptide antagonist of vasopressin receptor V2 with IC50 values of 1.2 and 2.3 nM for human afnd at V2, respectively.
Top Publications Citing Invivochem Products
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 473.93 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H21ClFN3O2 |
| CAS No. | 168079-32-1 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Lixivaptan displays competitive antagonist activity at V2 receptors |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In conscious dogs, water-loaded with 30 mL/kg (po) and arginine vasopressin (AVP)-treated (0.4 µg/kg in oil, sc), lixivaptan (1, 3, and 10 mg/kg po) increases Uvol over the AVP-treated vehicle group by 438, 1018, and 1133%, respectively, while Uosm decreases from 1222 mOsm/kg (water-loaded and AVP treated vehicle) to 307, 221, and 175 mOsm/kg, respectively. In homozygous Brattleboro rats lacking AVP, lixivaptan at 10 mg/kg po (i.e., 10 times the dose producing V2 antagonist activity) b.i.d. for 5 days, shows a sustained antagonist action without evidence of agonist effects. In a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled ascending single dose study, patients (deprived of fluids overnight before dosing) are dosed orally with 30, 75, or 150 mg of lixivaptan. All three doses increase urine flow and serum sodium concentrations and produced significant dose-related decreases in urinary osmolality |
These protocols are for reference only. InvivoChem does not
independently validate these methods.
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 2.1100 mL | 10.5501 mL | 21.1002 mL | 42.2003 mL |
| 5mM | 0.4220 mL | 2.1100 mL | 4.2200 mL | 8.4401 mL |
| 10mM | 0.2110 mL | 1.0550 mL | 2.1100 mL | 4.2200 mL |
| 20mM | 0.1055 mL | 0.5275 mL | 1.0550 mL | 2.1100 mL |
The molarity calculator equation
Mass(g) = Concentration(mol/L) × Volume(L) × Molecular Weight(g/mol)
Mass
=
Concentration
×
Volume
×
Molecular Weight*
The dilution calculator equation
Concentration(start)
×
Volume(start)
=
Concentration(final)
×
Volume(final)
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
Concentration(start)
C1
×
Volume(start)
V1
=
Concentration(final)
C2
×
Volume(final)
V2
Step One: Enter information below
Dosage mg/kg
Average weight of animals g
Dosing volume per animal µL
Number of animals
Step Two: Enter the in vivo formulation
%DMSO
+
%
+
%Tween 80
+
%ddH2O
Calculation Results:
Working concentration:
mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid:
mg
drug pre-dissolved in
µL
DMSO(Master liquid concentration
mg/mL)
,Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation:
Take
µL
DMSO master liquid, next add
µL
PEG300, mix and clarify, next add
µL
Tween 80,mix and clarify, next add
µL
ddH2O,mix and clarify.
Note:
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































