This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 25g | $180 | Check With Us |
| 50g | $240 | Check With Us |
| 100g | $360 | Check With Us |
Cat #: V2708 CAS #: 107-97-1 Purity ≥ 98%
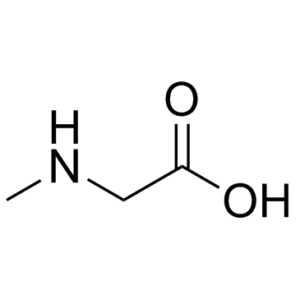
Description: Sarcosine [also called N-methylglycine, Sarcosinic acid, Methylaminoacetic acid, Methylglycine] is a competitive inhibitor of the type I glycine transporter (GlyT1) and an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) co-agonist. Sarcosine is a GlyR agonist in addition to being a GlyT1 inhibitor and NMDAR co-agonist, but it is less potent than glycine as a GlyR agonist and is not a full agonist. The viability of the sarcosine-treated cells is significantly reduced. Sarcosine has weak anticonvulsant properties.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 89.09 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO2 |
| CAS No. | 107-97-1 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder formr |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: <1 mg/mLr |
| Water: 17 mg/mL (190.8 mM)r | |
| Ethanol: <1 mg/mL | |
| Solubility In Vivo | O=C(O)CNC |
| Synonyms | N-methylglycine, Sarcosinic acid, Methylaminoacetic acid, Methylglycine; N-Methylaminoacetic acid; Sarcosin |
| Protocol | In Vivo | Sarcosine (400-800mg/kg; i.p.) significantly raises the threshold for electroconvulsions |
|---|---|---|
| Animal model | Albino Swiss mice weighing (25-30 g) | |
| Dosages | 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg, 400 mg/kg, 800 mg/kg | |
| Administration | Intraperitoneal injection |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 11.2246 mL | 56.1230 mL | 112.2460 mL | 224.4921 mL |
| 5mM | 2.2449 mL | 11.2246 mL | 22.4492 mL | 44.8984 mL |
| 10mM | 1.1225 mL | 5.6123 mL | 11.2246 mL | 22.4492 mL |
| 20mM | 0.5612 mL | 2.8062 mL | 5.6123 mL | 11.2246 mL |
| Quality Control Documentation |
|
|---|
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































