This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price | Stock |
|---|---|---|
| 10mg | $175 | 3-6 Days |
| 25mg | $350 | 3-6 Days |
| 50mg | $600 | 3-6 Days |
| 100mg | $990 | 3-6 Days |
Cat #: V41621 CAS #: 547-75-1 Purity ≥ 99%
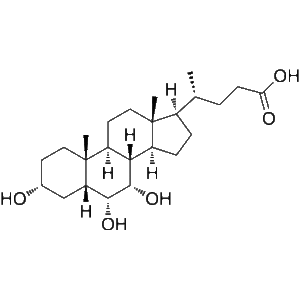
Description: Hyocholic Acid (3α,6α,7α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid) is a biliary acid found mainly in pig as well as in human urine at low concentrations, in particular, in urine samples from patients with cholestasis. Hyocholic Acid can promote GLP-1 secretion via activating TGR5 and inhibiting FXR in enteroendocrine cells. It is known for its exceptional resistance to type 2 diabetes . Hyocholic acid differs from the primary bile acids found in humans by having a third hydroxyl group in the α-conformation at the 6-position, unlike cholic acid, which has a 12-hydroxyl, and chenodeoxycholic acid which has neither a 6- or 12-hydroxyl. It also differs from the muricholic acids found in rodents, as they are 6β-hydroxylated, and can have the 7-hydroxyl in either the α- or β- positions, forming α- or β-muricholic acids.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Formula | C24H40O5, |
|---|---|
| CAS No. | 547-75-1 |
| Protocol | In Vitro | Hyocholic Acid/HCA (25 and 50 μM, 24 h) upregulates GLP-1 protein secretion in STC-1 and NCI-H716 cells[3]. HCA (25 and 50 μM, 24 h) upregulates proglucagon gene transcription in STC-1 and NCI-H716 cells[3]. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Line: NCI-H716 cells Concentration: 50 μM Incubation Time: 48 h Result: Inhibited the high expression of SHP (small heterodimer partner) induced by the FXR agonist. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | Hyocholic Acid/HCA (20 mg/kg, p.o.) suppresses BA depletion-induced blood glucose increase in pigs[3]. Hyocholic Acid (100 mg/kg/day, p.o.) improves serum fasting GLP-1 secretion and glucose homeostasis in diabetic mouse models[3]. Animal Model: BA depletion pigs[3] Dosage: 20 mg/kg Administration: Oral administration (p.o.) Result: Attenuated the increased blood glucose levels corresponding with GLP-1 decrease. Animal Model: db/db model, and the high-fat diet and streptozotocin (HFD+STZ) induced diabetic model[3] Dosage: 100 mg/kg/day Administration: Oral administration (p.o.) Result: Improved oral glucose tolerances shown by lower glucose levels. Increased circulating active GLP-1 levels and fasting insulin levels. |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































