This product is for research use only, not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
| Size | Price |
|---|---|
| 250mg | Get quote |
| 500mg | Get quote |
| 1g | Get quote |
Cat #: V5013 CAS #: 1621523-07-6 Purity ≥ 98%
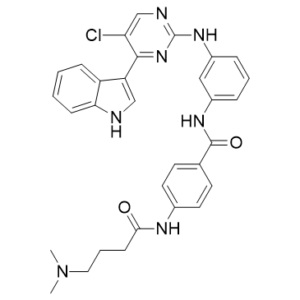
Description: THZ1-R is a novel and non-cysteine reactive analog of THZ1 which shows lower activity for CDK7 inhibition with a Kd of 142 nM for binding to CDK7. THZ1 is a novel, potent, selective and covalent CDK7 inhibitor which has the unprecedented ability to target a remote cysteine residue located outside of the canonical kinase domain, providing an unanticipated means of achieving selectivity for CDK7. THZ1 covalently modifies CDK7 by targeting C312 residue outside of the kinase domain, providing an unanticipated means of achieving covalent selectivity. THZ1 potently inhibits proliferation of Jurkat and Loucy T-ALL cell lines with IC50 values of 50nM and 0.55nM, respectively. In the kinase binding assay, THZ1 shows a good binding affinity with IC50 value of 3.2nM.
Publications Citing InvivoChem Products
Product Promise

- Physicochemical and Storage Information
- Protocol
- Related Biological Data
- Stock Solution Preparation
- Quality Control Documentation
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 568.07 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C₃₁H₃₀ClN₇O₂ |
| CAS No. | 1621523-07-6 |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility In Vitro | DMSO: > 100 mg/mL |
| Water: <1 mg/mL | |
| Ethanol: N/A | |
| Synonyms | THZ1-R; THZ1 R |
| Protocol | In Vitro | In vitro activity: THZ1 uses a unique mechanism, combining ATP-site and allosteric covalent binding, as a means of attaining potency and selectivity for CDK7. THZ1 irreversibly inhibits RNAPII CTD phosphorylation by covalently targeting a unique cysteine located outside the kinase domain of CDK7. THZ1, but not THZ1-R, completely inhibits the phosphorylation of the established intracellular CDK7 substrate RNAPII CTD at Ser 5 and Ser 7, with concurrent loss of Ser 2 phosphorylation at 250 nM in Jurkat cells. THZ1 exhibits strong antiproliferative effects across a broad range of cancer cell lines from various cancer types. In Jurkat cells, low-dose THZ1 has a profound effect on a small subset of genes, including the key regulator RUNX1, thus contributing to subsequent loss of the greater gene expression program and cell death. THZ1 causes defects in Pol II(polymerase II) phosphorylation, co-transcriptional capping, promoter proximal pausing, and productive elongation. Kinase Assay: THZ1 is a novel selective and potent covalent CDK7 inhibitor with IC50(binding affinity) of 3.2 nM. Cell Assay: Cells (Jurkat, Loucy, KOPTK1 and DND-41 cell lines) are treated with THZ1, THZ1-R or dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO) for 0-6 h to assess the effect of time on the THZ1-mediated inhibition of RNAPII CTD phosphorylation. For subsequent experiments cells are treated with compounds for 4 h as determined by the time-course experiment described earlier, unless otherwise noted. For inhibitor washout experiments, cells are treated with THZ1, THZ1-R or DMSO for 4 h. Medium containing inhibitors is subsequently removed to effectively 'washout' the compound and the cells are allowed to grow in the absence of inhibitor. For each experiment, lysates are probed for RNAPII CTD phosphorylation and other specified proteins. |
|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | THZ1 reduces the proliferation of KOPTK1 T-ALL cells in a human xenograft mouse model. THZ1 is well tolerated at 10 mg/kg with no observable body weight loss or behavioural changes, suggesting that it causes no overt toxicity in the animals | |
| Animal model | Bioluminescent xenografted mouse model |
| Solvent volume to be added | Mass (the weight of a compound) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mother liquor concentration | 1mg | 5mg | 10mg | 20mg |
| 1mM | 1.7603 mL | 8.8017 mL | 17.6035 mL | 35.2069 mL |
| 5mM | 0.3521 mL | 1.7603 mL | 3.5207 mL | 7.0414 mL |
| 10mM | 0.1760 mL | 0.8802 mL | 1.7603 mL | 3.5207 mL |
| 20mM | 0.0880 mL | 0.4401 mL | 0.8802 mL | 1.7603 mL |
This equation is commonly abbreviated as: C1 V1 = C2 V2
- (1) Please be sure that the solution is clear before the addition of next solvent. Dissolution methods like vortex, ultrasound or warming and heat may be used to aid dissolving.
- (2) Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order.




































